Building a Scalable 3-Tier Architecture on AWS Using Terraform: A Modular Approach
In this project, we will design and implement a scalable three-tier architecture on AWS using Terraform. The setup follows a modular approach, organizing infrastructure into separate layers: Core, Web, App, and Database. This ensures better manageability, reusability, and security while deploying cloud resources. By the end, you will have a fully automated, infrastructure-as-code (IaC) solution for hosting applicatio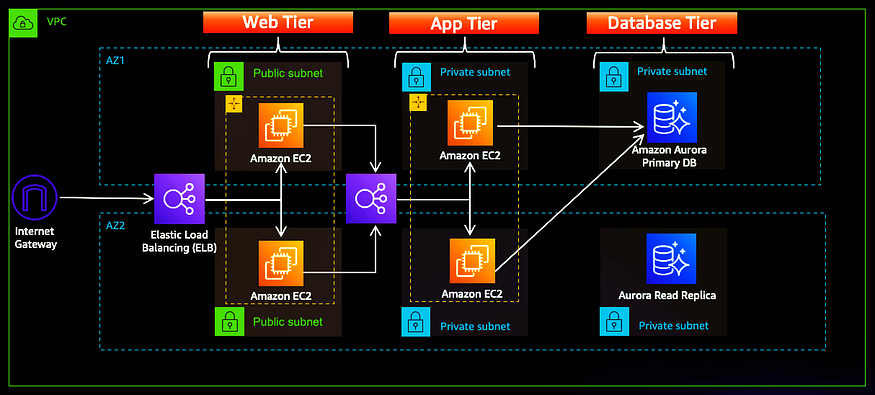 ns on AWS.
ns on AWS.
GitHub link: https://github.com/Consultantsrihari/3-Tier-Architecture-on-AWS-Using-Terraform.git
Prerequisites
Before starting this project, ensure you have the following:
✅ AWS Account — To provision cloud resources using Terraform.
✅ Terraform Installed — Download and install Terraform on your local machine.
✅ AWS CLI Installed & Configured — Install AWS CLI and run aws configure to set up credentials.
✅ IAM User with Required Permissions – Ensure your IAM user has permissions to create and manage VPCs, EC2, RDS, ALB, and other AWS resources.
✅ Basic Knowledge of Terraform – Familiarity with writing .tf files, providers, modules, and variables.
✅ Code Editor (VS Code Recommended) – Use VS Code with the Terraform extension for syntax highlighting and better development experience.
✅ Git Installed (Optional) – For version control and managing Terraform code in a GitHub repository.
Architecture Overview
We will deploy a three-tier architecture consisting of the following:
- VPC (Core Layer): Contains public and private subnets.
- Public Subnets: Bastion Host & NAT Gateway.
- Private Subnets: Web/Application servers (EC2 instances) and Database (Amazon RDS).
- Load Balancer: ALB to distribute traffic.
- Security Groups: Restricted access at different layers.
Project Structure:-

Root Module (main.tf)
module "core" {
source = "./modules/core"
vpc_cidr = "10.0.0.0/16"
public_subnet_cidrs = ["10.0.1.0/24", "10.0.2.0/24"]
private_subnet_cidrs = ["10.0.3.0/24", "10.0.4.0/24"]
db_subnet_cidrs = ["10.0.5.0/24", "10.0.6.0/24"]
azs = ["us-east-1a", "us-east-1b"]
}
module "web" {
source = "./modules/web"
public_subnet_ids = module.core.public_subnet_ids
web_alb_sg_id = module.core.web_alb_sg_id
web_instance_sg_id = module.core.web_instance_sg_id
web_ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0"
web_instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
module "app" {
source = "./modules/app"
private_subnet_ids = module.core.private_subnet_ids
app_alb_sg_id = module.core.app_alb_sg_id
app_instance_sg_id = module.core.app_instance_sg_id
app_ami = "ami-0c55b159cbfafe1f0"
app_instance_type = "t2.micro"
}
module "database" {
source = "./modules/database"
db_subnet_ids = module.core.db_subnet_ids
db_sg_id = module.core.db_sg_id
db_name = "mydb"
db_user = "admin"
db_password = "securepassword123"
}Security Group Setup
sg.tf
# Web ALB Security Group
resource "aws_security_group" "web_alb" {
name = "web-alb-sg"
description = "Allow HTTP inbound traffic"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
ingress {
from_port = 80
to_port = 80
protocol = "tcp"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
egress {
from_port = 0
to_port = 0
protocol = "-1"
cidr_blocks = ["0.0.0.0/0"]
}
}
# Database Security Group
resource "aws_security_group" "database" {
name = "db-sg"
description = "Allow MySQL access from app tier"
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
ingress {
from_port = 3306
to_port = 3306
protocol = "tcp"
security_groups = [module.core.app_instance_sg_id]
}
}1. Core Network Module (modules/core)
main.tf
resource "aws_vpc" "main" {
cidr_block = var.vpc_cidr
tags = {
Name = "3tier-vpc"
}
}
# Public Subnets
resource "aws_subnet" "public" {
count = length(var.public_subnet_cidrs)
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = var.public_subnet_cidrs[count.index]
availability_zone = var.azs[count.index]
tags = {
Name = "public-subnet-${count.index}"
}
}
# Private Subnets (App Tier)
resource "aws_subnet" "private" {
count = length(var.private_subnet_cidrs)
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = var.private_subnet_cidrs[count.index]
availability_zone = var.azs[count.index]
tags = {
Name = "private-subnet-${count.index}"
}
}
# Database Subnets
resource "aws_subnet" "database" {
count = length(var.db_subnet_cidrs)
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
cidr_block = var.db_subnet_cidrs[count.index]
availability_zone = var.azs[count.index]
tags = {
Name = "db-subnet-${count.index}"
}
}
# Internet Gateway
resource "aws_internet_gateway" "gw" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
}
# NAT Gateway
resource "aws_nat_gateway" "nat" {
allocation_id = aws_eip.nat.id
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public[0].id
}
resource "aws_eip" "nat" {
vpc = true
}
# Route Tables
resource "aws_route_table" "public" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
gateway_id = aws_internet_gateway.gw.id
}
}
resource "aws_route_table" "private" {
vpc_id = aws_vpc.main.id
route {
cidr_block = "0.0.0.0/0"
nat_gateway_id = aws_nat_gateway.nat.id
}
}
# Subnet Associations
resource "aws_route_table_association" "public" {
count = length(var.public_subnet_cidrs)
subnet_id = aws_subnet.public[count.index].id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.public.id
}
resource "aws_route_table_association" "private" {
count = length(var.private_subnet_cidrs)
subnet_id = aws_subnet.private[count.index].id
route_table_id = aws_route_table.private.id
}2. Web Tier Module (modules/web)
main.tf
resource "aws_lb" "web" {
name = "web-alb"
internal = false
load_balancer_type = "application"
security_groups = [var.web_alb_sg_id]
subnets = var.public_subnet_ids
}
resource "aws_launch_template" "web" {
name_prefix = "web-"
image_id = var.web_ami
instance_type = var.web_instance_type
key_name = var.key_name
network_interfaces {
security_groups = [var.web_instance_sg_id]
}
user_data = base64encode(<<-EOF
#!/bin/bash
yum install -y nginx
systemctl start nginx
EOF
)
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "web" {
desired_capacity = 2
max_size = 4
min_size = 2
vpc_zone_identifier = var.public_subnet_ids
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.web.id
version = "$Latest"
}
}3. Application Tier Module (modules/app)
main.tf
resource "aws_lb" "app" {
name = "app-alb"
internal = true
load_balancer_type = "application"
security_groups = [var.app_alb_sg_id]
subnets = var.private_subnet_ids
}
resource "aws_launch_template" "app" {
name_prefix = "app-"
image_id = var.app_ami
instance_type = var.app_instance_type
key_name = var.key_name
network_interfaces {
security_groups = [var.app_instance_sg_id]
}
}
resource "aws_autoscaling_group" "app" {
desired_capacity = 2
max_size = 4
min_size = 2
vpc_zone_identifier = var.private_subnet_ids
launch_template {
id = aws_launch_template.app.id
version = "$Latest"
}
}4. Database Tier Module (modules/database)
main.tf
resource "aws_db_subnet_group" "db" {
name = "db-subnet-group"
subnet_ids = var.db_subnet_ids
}
resource "aws_db_instance" "main" {
allocated_storage = 20
storage_type = "gp2"
engine = "mysql"
engine_version = "5.7"
instance_class = "db.t2.micro"
db_name = var.db_name
username = var.db_user
password = var.db_password
parameter_group_name = "default.mysql5.7"
skip_final_snapshot = true
db_subnet_group_name = aws_db_subnet_group.db.name
vpc_security_group_ids = [var.db_sg_id]
}Deployment Steps
1️. Initialize Terraform
terraform init2️. Plan the Deployment
terraform plan3️. Apply the Configuration
terraform apply -auto-approve4. Verify the Deployment
- Check AWS Console for created resources.
- Validate EC2 instances, ALB, and RDS.
5️.Destroy Infrastructure
terraform destroy -auto-approveKey Components:
- Web Tier: Public-facing ALB with Auto Scaling EC2 instances
- App Tier: Internal ALB with private EC2 instances
- Database Tier: MySQL RDS instance in isolated subnets
- Network: VPC with public, private, and database subnets
- Security: Security groups for each tier with least-privilege access
This architecture provides:
- Horizontal scaling with Auto Scaling Groups
- High availability across AZs
- Network isolation between tiers
- Secure communication between components
- Managed database service with RDS
Conclusion:
This Terraform-driven 3-tier AWS deployment establishes a scalable, secure, and highly available architecture, leveraging infrastructure-as-code (IaC) best practices. By modularizing components (web, app, database) and isolating network layers, it ensures fault tolerance, simplified maintenance, and controlled access between tiers. The use of auto-scaling groups, ALBs, and RDS guarantees resilience and performance, while security groups enforce least-privilege principles. This foundation supports seamless scaling, cost optimization, and compliance readiness, providing a robust blueprint for modern cloud-native applications. Future enhancements like HTTPS, WAF, or secrets management can further strengthen production readiness.
………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………………
You’re welcome! Have a great time ahead! Enjoy your day!
Please Connect with me any doubts.
Mail: sriharimalapati6@gmail.com
LinkedIn: www.linkedin.com/in/
GitHub: https://github.com/Consultantsrihari
Medium: Sriharimalapati — Medium
Comments
Post a Comment